Is saunders research onion making you curious? If yes, then hold on to this article for a few minutes. This is a guide for beginners on how to structure a research methodology by using saunders research onion.
So, If you are someone who has a tough time in constructing “methodology”. Or your mind just doesn’t work to figure out the future course of action, you must invest your time here.
The methodology is one of the crucial parts of a research paper. This chapter has the power to underpin the whole paper and add credibility to it. Thus, you must prepare it with immense care by measuring all the possible decisions. Now, let’s move to know how the concept of research onion can help you in drafting a better research methodology.
What is the saunders research onion?
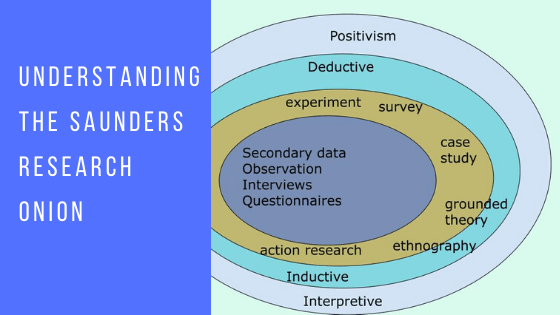
Saunders Research Onion is one of the most popular models in academia. There are a lot of researchers who resort to this when it comes to drafting the highly-feared “methodology” chapter. Saunders et al developed this model in 2007. Named after the founder, it has various layers. It represents the different stages which lead a researcher to build a striking methodology. While passing through all the stages there is one thing which needs your focus. You should measure every possibility to make a logical decision. This is all that turns into credible research.
Basically, research onion has six layers. By now, you must be thinking about the analogy of this model to research methodology. Well, to understand the analogy you only need to focus on the structured process of peeling. Still unclear? Let’s understand it this way:
We all have seen onions. Right? Peeling the layers of onion from the outer side, one after another eventually leads to its core. Now, this is exactly what you need to follow with Saunders research onion model. To reach a perfect methodological decision you will have to begin with the outermost layer of research philosophy (research onion). After this, you will have to move to the middle layers consisting of research strategies, approaches, choices and time spans. By peeling Saunders’ research onion eventually, you will hit the core, i.e. research procedures and techniques.
Don’t forget to pay attention to every layer of the research onion. Each of them has something important. Each of them has some or other element which can enrich your thesis or dissertation. So, make sure you don’t ignore any layer no matter what comes in your way. Now that you have got an introduction to Saunders’ model, let’s move to know layers of this research onion in detail:
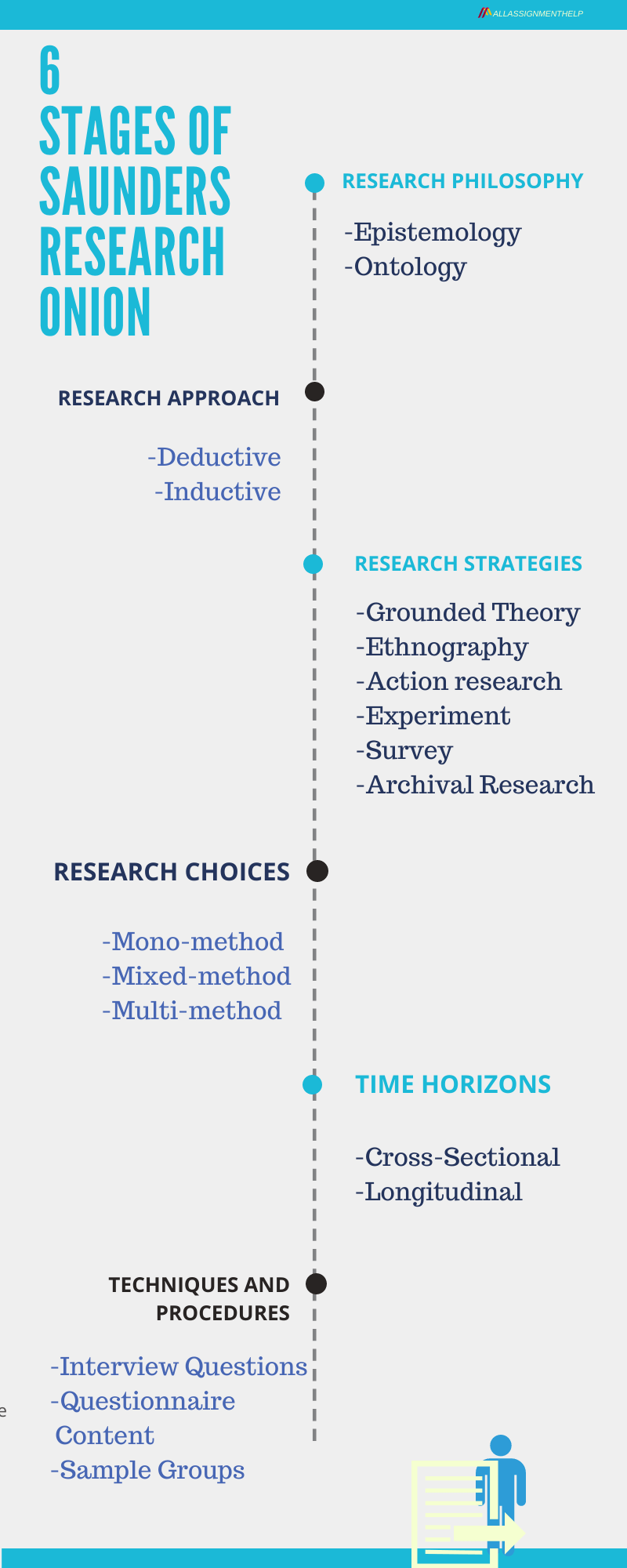
Saunders Research Onion Stage 1: Research philosophy
Research philosophy is the outermost layer of the Saunders research onion. It is related to a set of beliefs on the nature of the investigation of reality. It is often studied in the context of epistemology and ontology. While researching, you must explore it with care. The selection philosophical stance may impact the gathering of data and its analysis. Let’s move to know what epistemology and ontology are.
Epistemology
Epistemology is the branch of philosophy dealing with the question of what should be considered as acceptable knowledge in different disciplines. Also, how one can attain it. Basically, it ends up in answering all the questions starting from “what” and “how”. As per Epistemology, researchers consider below-listed elements as a source of knowledge:
- Sensation
- Perception
- Reason,
- Faith
- Intuition
If this branch of philosophy is still unclear to you, have a glance at some elements known as critical realism, interpretivism and positivism. They are the philosophical stances which connect to Epistemology.
Positivism
The position of positivism is completely based on an idea that says scientific knowledge is acceptable knowledge of this world. It further assures that scientific knowledge is true and characterized by the test of research questions (hypothesis) which are derived from the pre-existing theories. The main body research created through positivism can be replicated with similar quantifiable outcomes which comes from statistical analysis.
Realism
This philosophical stance raises questions about the reliability of scientific knowledge. Unlike positivism, it does not completely support scientific knowledge. It helps in maintaining the fact that all theories may not be ultimately true or complete. It states that they can be revised at any point in time. As per realism, consistent research and adoption of new methods of research can bring more reliable results in comparison to the existing theories. In this stance, the newly adopted methods of research add to true knowledge.
Critical Realism or interpretivism
An interpretive philosophy. Unlike positivism and realism, it emphasizes the usage of qualitative research analysis over statistical analysis or quantitative analysis to get the final outcomes. The researchers who follow this philosophical stance can be observed playing a vital role in interpreting the gathered data and making sense out of it. Thus, it is said that interpretivism successfully recognizes the difference among people. It also incorporates a human interest in a research study.
Ontology
Ontology deals with the study of reality or things which publicly display a reality. It is a branch of metaphysics which answers the questions based on “what is”. There are a number of elements which represents ontology or inventory around us. Some of them are minds, properties, abstract entities, numbers and sets, values, physical objects etc.
A brief introduction of pragmatism, constructivism and objectivism which constitute Ontology can give you a broader and better insight to you. So, let’s have a look at them:
Objectivism
It was derived from the belief that values and knowledge of humans and determined by the nature of reality and they are objective as well. They are not generated from opinions or thoughts which an individual has. Let’s this with an example, suppose that it is a sunny day, it would be for real and every living creature in that specific area would acknowledge the same. This kind of realities is not dependant on human views or thoughts of any individual (social actor). It leaves an impact on them.
Constructivism
Constructivism deals with the question of how bodies of knowledge originated. It focuses on how different ideas and beliefs are established by human decisions and interactions. Unlike objectivism, the philosophical stance restates that reality is framed by social actors or it is dependant on their actions. For instance, a new regulation passed by any government may or may not be the result of some people (social actors).
Pragmatism
Under this philosophical stance, the focus remains on the connection of practice and theories. Pragmatism strongly asserts that both the above-listed stances, constructivism and objectivism are valid and practical. There are ways to approach research and both these above-mentioned stances can take a researcher to solutions to problems.
Saunders Research Onion Stage 2: Research approach
In the second layer of research onion, you get the demonstration of approaches which a researcher can resort to while carrying out any type of research.
According to Saunders’ Research Onion, a research approach can be inductive or deductive. It selection completely depends on the earlier research aims, personal opinions, limitations, choices etc.
Deductive
The deductive approach flows from generic to specific. The researchers who use deductive reasoning usually begin their theory and move towards hypotheses or questions which are tested via data collection. The outcomes derived from the gathered data either confirms or rejects the hypothesis.
Inductive
Under this research approach is helpful and it is often used when the dissertation requires little or no research on the subject in question. Unlike deductive reasoning, you will have to go in the opposite way from the main question to description and observation to analysis.
Saunders Research Onion Stage 3: Research Strategies
The third layer of research philosophy revolves around how a researcher plan to gather data for the dissertation. The data collection methods may include case studies, grounded theory, experiment, action research, surveys, archival research etc. Being an academic researcher you can select more than one methods. Saunders’ research strategies help in making your work as a researcher easy.
Saunders Research Onion Stage 4: Research Choices
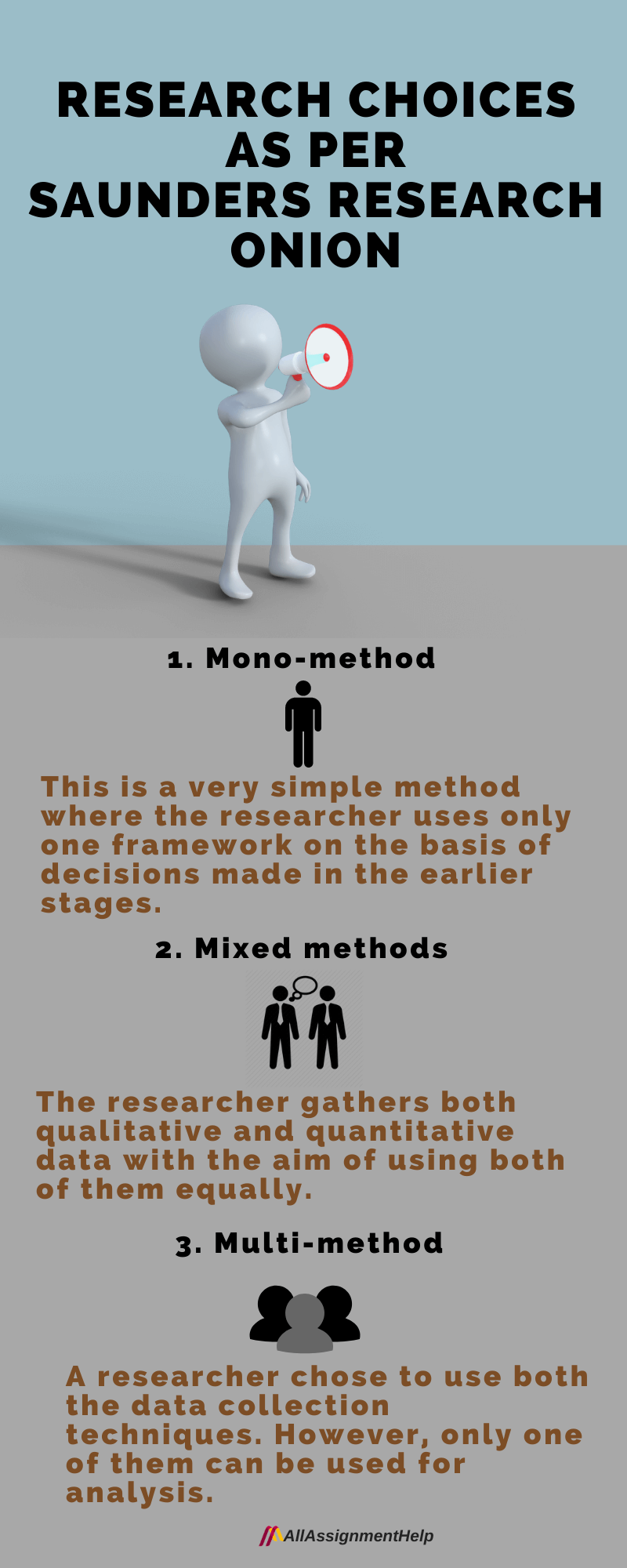
The fourth stage or level of this research onion deals with quantitative and qualitative methodologies. At this stage, you will have to reach a decision whether you would select the former or latter for your dissertation. You can also use both methods, however, in case you are using both of them, you will need to decide whether they would be measured equally or not.
Here you will have to follow a set framework of tools and methods which will depend on the choices you make at this fourth stage of research onion.
Generally, there are three methods to select while working with this specific layer of Saunder’s research onion, they are:
Mono-method
This is a very simple method where the researcher uses only one framework. You can choose this method on the basis of decisions made in the earlier stages of research onion.
Mixed methods
Here, a researcher gathers both qualitative and quantitative data with the aim of using both of them equally. If you choose this method you will have to use both data collection and data analysis equally. This is why this research is called as mixed-method research. The main focus of this framework lies in trying to complement qualitative data with quantitative data so that the limitations of both methods can be overruled.
Multi-method
Under this one, the researcher chose to use both the data collection techniques. This means that being a researcher you can collect data through both quantitative and qualitative data. However, you can use only one of them of the overall analysis of data.
Saunders Research Onion Stage 5: Time Horizons
Time Horizon is the fifth layer of the Saunders Research Onion. It is the specific time-period which your professor allot you for the completion of a specific project. Some thesis assignment experts suggest that as a researcher, you must know which time-frame is suitable for your dissertation. Saunder’s research onion has two options for researchers as there are two types of time horizons:
Cross-sectional
This time-frame represents a snapshot view of a specific circumstance at a particular point. It also confines the time-limit of research and data collection to a comparatively shorter time period.
Longitudinal
This research studies and revolves around the behaviours by the use of concentrated samples over a subsequent period of time.
Saunders Research Onion Stage 6: Techniques and Procedures
The last layer of research onion is where you find techniques and procedures. You can also consider it as the core of this onion. At this stage, you will have to focus on data collection and data analysis. Being a researcher, it will be easier for you to jot down your decisions regarding interview questions, ethics, questionnaire content, sample groups and other similar things in this specific section. Another thing which you will remember is that all the decisions from the fifth layer should according to the previous layers of the Saunders’ onion. Otherwise, you will never end up in generating valid outcomes.
We have reached the end stage and I hope that this article really served as a guide for beginners. I hope all your doubts regarding Saunders’ research onion and research methodology are clear now. It would be overwhelming if you will share your views on how the research onion for dummies has been explained here.
Lastly, if it is still being tough for you to come up with an effective methodology, or any other chapter of your dissertation, go and consult an expert. You can always ask for help with the dissertation without thinking twice. Feel free to ping us for any kind of assistance with your thesis or dissertation.
Q & A
Can you name some Saunders research onion research strategies?
There are the following research strategies in Saunders research onion:
- Grounded Theory
- Ethnography
- Action research
- Experiment
- Survey
- Archival Research
If you want to know detailed explanation of any of these research strategies you can get in contact with the experts of AllAssignmentHelp.co.uk.
What is the research onion by saunders?
It is model by Saunders et al. He developed it to facilitate the process of making “methodology”. It has six layers. Namely:
- Research Philosophy
- Approach for research
- Research strategies
- Choices for research
- Time Frame
- Techniques and Procedures
Why use saunders research onion?
You can use this model by Saunders if you fear to prepare methodology. It provides a clear picture of all the facts and future course of actions. This is what makes the process of making an effective research methodology easy.